As a business grows, management tasks may become overwhelming for entrepreneurs. To solve this issue, businesses turn to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). They are the two most common software allowing businesses to manage their resources more efficiently. Yet, many want to compare ERP vs CRM to conclude which one works better for their company.
Picture a scenario where every decision made must not only optimize internal processes but also resonate with the diverse needs of a customer base hungry for personalized experiences. This is a matter of fact – the intersection of ERP and CRM.
In this exploration, we will explore the essentials of ERP vs CRM, understanding their unique roles and how they can redefine the landscape for businesses of all sizes.
Contents
What is ERP?
ERP is a comprehensive software solution designed to streamline and integrate business processes and information across an entire organization. ERP systems are built to manage various aspects of business operations, including finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and more. The goal of an ERP system is to enhance efficiency, reduce manual efforts, and provide a centralized platform for data and process management.
How does ERP work?
ERP functions as a centralized system housing a singular database, facilitating the seamless coordination of core business processes. This integrated approach allows employees to concentrate on handling valuable data efficiently.
The real-time updating and standardized information retrieval within ERP significantly contribute to minimizing errors and expediting processes. Issues are swiftly directed to the respective responsible individuals, enhancing the overall efficiency of the system.

ERP extends its influence across various business facets, encompassing inventory and order management, supply chain systems, production, distribution, fulfillment, e-commerce, HR management, and customer service. This all-encompassing scope ensures that the entire spectrum of business operations is interconnected for optimal performance.
The implementation of role-based functionality within ERP is pivotal. This feature restricts access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can retrieve specific information. Not only does this enhance audit tracking capabilities, but it also acts as a proactive measure in mitigating potential risks associated with unauthorized access.
Benefits of ERP
- Integrated Business Processes: ERP systems integrate various business processes, such as finance, human resources, inventory management, and supply chain. This integration eliminates data silos and improves overall efficiency.
- Increased Productivity: By automating repetitive tasks and providing real-time information, ERP systems enhance productivity. Employees can focus on more value-added activities, and decision-makers have access to accurate data for better decision-making.
- Cost Savings: ERP systems help in cost reduction by optimizing business processes, reducing manual errors, and improving resource utilization. This leads to lower operational costs and better financial management.
- Improved Reporting and Planning: ERP software provides robust reporting and analytics tools, enabling organizations to generate detailed reports on various aspects of their operations. This supports strategic planning and decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems often include features to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. This is particularly important in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, where adherence to regulations is crucial.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to scale with the growth of the business. As companies expand, the ERP system can adapt to handle increased data volumes and additional business functionalities.
ERP Software Examples
Sage Business Cloud Enterprise Management
Sage Business Cloud Enterprise Management is a premier choice for businesses seeking industry-specific features. With an elastic, multi-company structure, parameterized system, and robust approval and audit engines, the platform provides customizable solutions. It centralizes operations from supply chain to sales, offering flexibility for diverse organizational needs. However, potential challenges include the cumbersome search for older transactions and integration issues with specific third-party applications.
Key Features
Sage Business Cloud excels in supply chain management, providing a real-time view and aiding in decision-making. The platform’s warehouse and inventory management features offer insights into inventory processes, warehouse operations, and order-to-cash cycles.
As a mobile-optimized system deployed in the cloud, it ensures accessibility from various devices. The platform simplifies project management by tracking projects, and budgets, and providing costing information.
Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite excels in providing real-time data access with flexibility through add-on modules and user seats, empowering businesses to tailor the system to their needs. Its robust business intelligence backbone ensures unified order-to-billing-to-revenue recognition on the cloud, streamlining critical processes, including comprehensive workflow and people management functionalities.
Considerations include higher pricing for add-ons and the absence of a free trial, potentially posing challenges for novices due to a complex interface.
Key Features
NetSuite’s unified suite seamlessly integrates ERP/financials, CRM, and e-commerce, offering global business management tools for consistent financial management. Supporting both B2C and B2B e-commerce, NetSuite facilitates omnichannel commerce with analytics and reporting tools for actionable insights. It efficiently manages human resources and streamlines project and resource management processes through professional services automation.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud
SAP, a global scalability leader, stands out as a top-tier solution designed to enhance operational efficiency worldwide. Renowned for real-time data insights, it empowers businesses to make informed decisions and adapt swiftly to market changes. The platform excels in standardized content for global use, ensuring consistency in diverse business environments, and boasts compatibility with major cloud platforms for flexibility. Offering a wide range of modules and automating maintenance-related tasks, SAP is a comprehensive global solution.
Key Features
SAP S/4HANA Cloud facilitates a seamless transition from product to service-based models, with industry-specific processes tailored for various sectors. Intelligent automation optimizes operations, emphasizing sustainability integration to reduce environmental impact. Ensuring compliance and security with global standards, SAP’s scalable platform, supported by a network of partners, adds value by adapting to evolving business needs.
What is CRM?
CRM focuses specifically on managing interactions and relationships with customers. CRM software is designed to help businesses organize, track, and analyze customer interactions throughout the customer lifecycle.
It typically includes features for managing customer contacts, sales leads, opportunities, and customer service interactions. The primary objective of CRM is to improve customer satisfaction, retain existing customers, and facilitate sales and marketing efforts
How does CRM work?

CRM operates as a meticulous recorder of every interaction between businesses and their customers, creating a comprehensive log of customer-related activities. For instance, when a salesperson engages in a cold call, the details of the conversation become a crucial part of the CRM record.
Subsequently, marketers leverage this information to tailor marketing strategies aimed at converting leads into customers.
Its ability to facilitate swift issue resolution in customer service. By maintaining a standardized and easily accessible data repository across departments, businesses can promptly identify and address any challenges that arise in customer interactions.
The true value of CRM is apparent in its role as a centralized repository of customer data and interactions. This wealth of information becomes a strategic asset for businesses. The marketing team, armed with analytics, gains deeper insights into their target segments, enabling the formulation of well-informed and targeted strategies.
Benefits of CRM
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM systems help businesses build and maintain strong relationships with customers by providing a centralized database of customer information. This allows organizations to better understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Enhanced Communication: CRM facilitates better communication within the organization, enabling teams to collaborate on customer-related activities. This leads to more effective sales, marketing, and customer service efforts.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: By tracking customer interactions and managing sales leads, CRM systems contribute to more efficient sales processes. They help sales teams prioritize leads, close deals faster, and identify upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
- Customer Data Analysis: CRM software provides tools for analyzing customer data, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on customer trends and behaviors. This data-driven approach supports targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences.
- Enhanced Customer Service: CRM systems streamline customer service processes by providing a centralized platform for managing customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests. This results in faster response times and improved customer satisfaction.
CRM Software Examples
Shape CRM
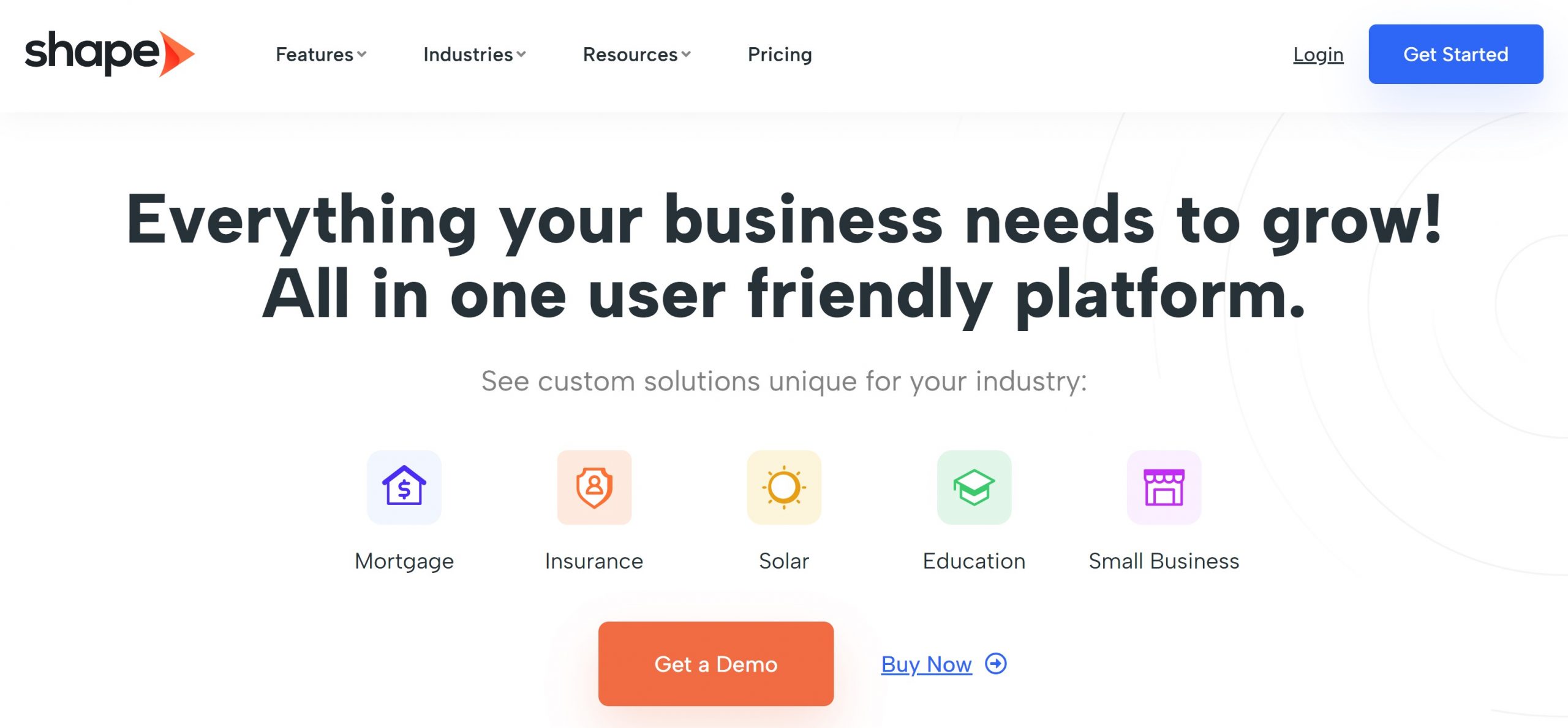
Shape CRM, acclaimed for its flexibility, holds a commendable rating of 4.4/5. Notable for its user-friendly interface, daily onboarding and training webinars, and prioritized list views, Shape CRM is designed for optimum user experience. The platform offers a robust phone dialer and operates on a flat fee structure, ensuring transparent pricing. While the eSignature functionality could see improvements, it’s essential to consider the higher price point associated with the platform.
Key Features
Shape CRM’s lead engine encompasses landing pages, lead distribution, automated scheduling, and more. The built-in phone dialer enhances communication with call tracking, live monitoring, and intelligent call routing. Additionally, the platform incorporates AI features like a chatbot, transcription assistant, and a text and image generator.
Zoho
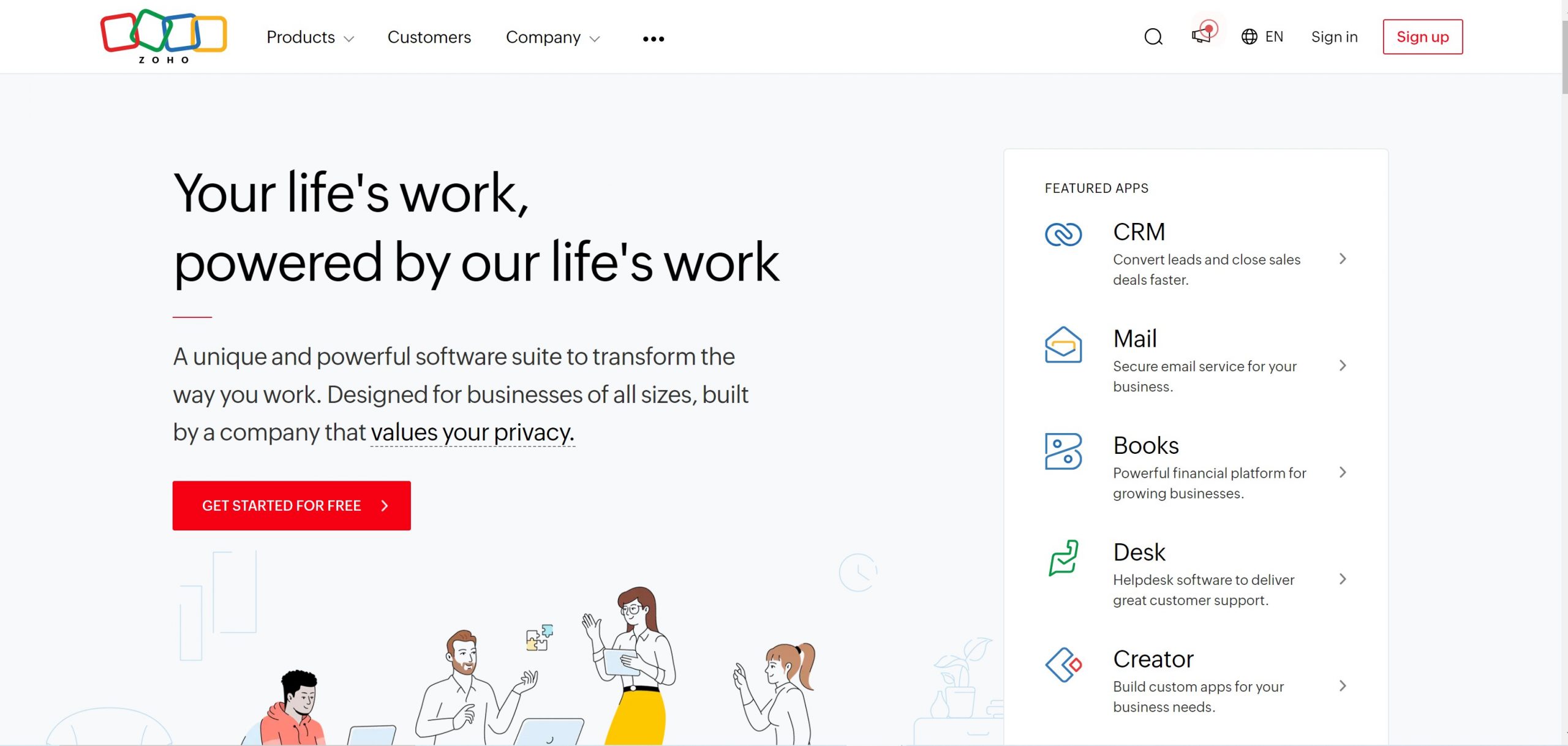
Zoho, recognized for its excellence in supporting decentralized teams, boasts a rating of 4.5/5. This platform prioritizes remote-first functionality, offering robust collaboration tools tailored for dispersed teams. With additional tool sets catering to critical business needs, Zoho is a valuable choice for organizations with decentralized structures. However, it’s crucial to note that free/low-cost plans may have reduced functionality.
Key Features
Zoho CRM stands out with its AI-powered sales Assistant, Zia, which predicts trends, anomalies, and conversions for smarter sales forecasting. The SalesSignals feature ensures real-time notifications across multiple channels, preventing missed interactions. The Blueprint functionality aids businesses in designing and automating their sales processes, providing clarity at each stage of a deal. With multi-channel support for various communication modes, including phone, email, live chat, social media, and in-person meetings, Zoho keeps teams connected seamlessly.
HubSpot
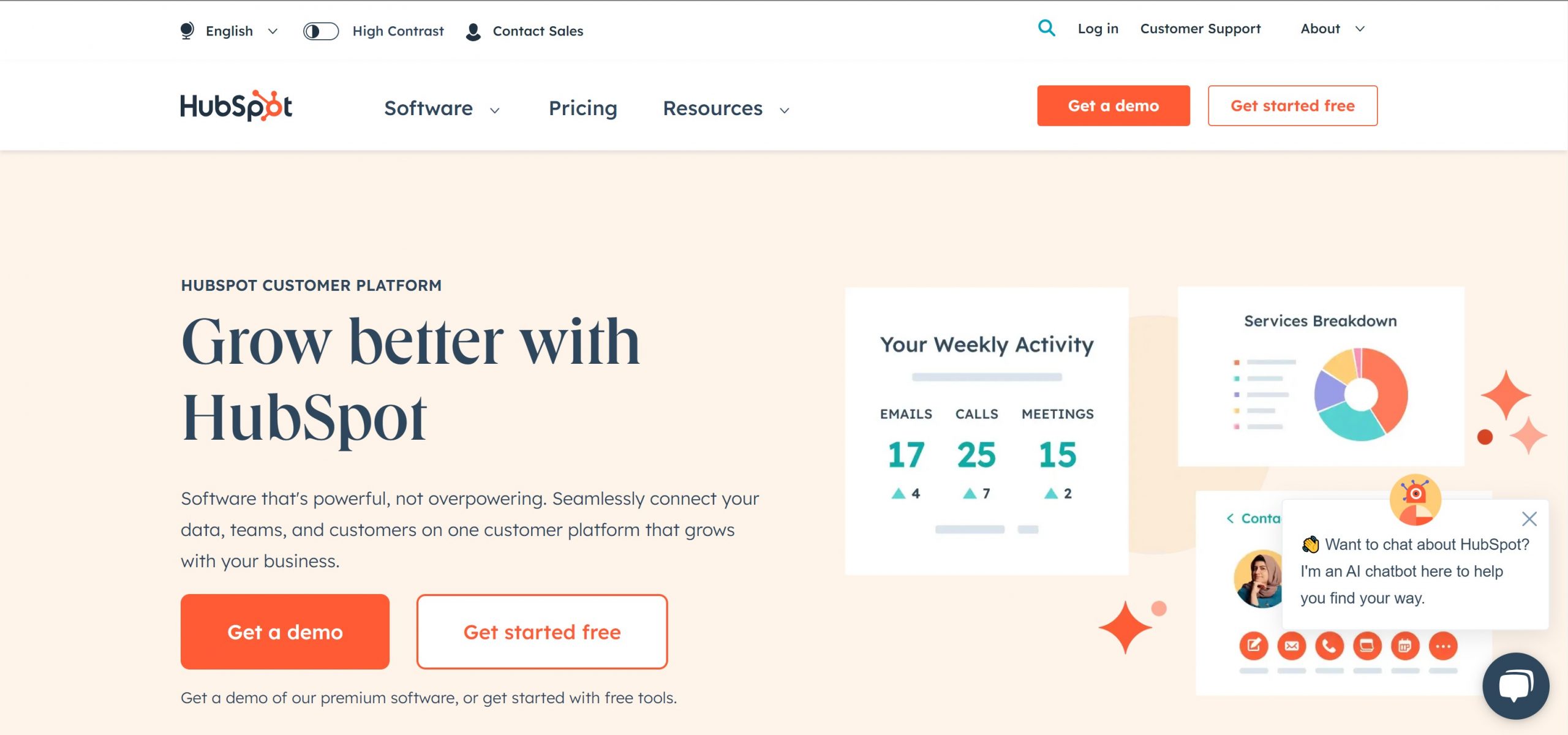
HubSpot, renowned for its CRM integration options, is a trusted industry name with a rating of 4.5/5. Offering first-class automation and integration choices, HubSpot consolidates CRM, email marketing, and website management in one platform, providing users with a comprehensive solution. While the free plan is a notable advantage, it’s essential to consider the higher-end cost structure for paid plans and additional tools, making HubSpot most suitable for use cases that demand more than just CRM software.
Key Features
HubSpot CRM excels in contact management, providing a detailed view of interactions and facilitating easy customer relationship management. Email tracking and notifications offer real-time updates, enhancing follow-up strategies. The platform’s visual dashboard aids in pipeline management, effectively tracking deals and stages. With a tool for simplified meeting scheduling, users can sync calendars and allow contacts to book time directly.
The Difference Between CRM and ERP
While the entire organization will come to rely on both ERP and CRM systems, the fundamental difference between the two is that ERP is primarily for financial data and the finance department, whereas CRM is customer data used by the sales and customer service departments. The former is referred to as the back office, and the latter as the front office.
Some ERP systems include a CRM component while others do not, but CRM software systems do not include ERP components. Salesforce, for example, is not an ERP system because it does not deal with transactional data. It may access order history or invoices, but this information is obtained through an integration with the ERP system.
ERP and CRM Integration

The integration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems has become increasingly vital. This synergy creates a unified approach to managing internal processes and external customer interactions, fostering operational efficiency and enriching customer relationships.
Understanding Integration Options
Businesses can explore pre-built connectors for quick adoption, opt for custom integration platforms tailored to complex systems, or leverage API-driven integrations for granular control and scalability. Careful consideration of organizational needs, budget constraints, and future growth plans is crucial in selecting the most suitable integration platform.
Crafting the Integration Strategy
With the integration platform chosen, the next step involves architecting a cohesive strategy. Visualization of seamless data flow between ERP and CRM is essential, breaking down silos to offer a holistic view of the business. Task automation enhances efficiency, and real-time visibility empowers informed decision-making. Adopting a customer-centric approach ensures personalized interactions and fosters loyalty.
Unlocking Benefits
ERP-CRM integration unlocks a myriad of benefits for businesses. It enhances customer experience through personalized offers, faster responses, and streamlined interactions. Operational efficiency receives a boost with real-time data and automated workflows, reducing errors and enhancing productivity.
While the promises of integration are substantial, challenges exist. Considerations include the cost and complexity of implementation, ensuring data quality and consistency between systems, and addressing change management issues. These challenges require thoughtful planning and execution to maximize the benefits of integration.
FAQ
Does ERP replace CRM?
ERP does not serve as a replacement for CRM. They are distinct entities within the framework of business operations. ERP focuses on the back office, like managing finances, inventory, and operations. CRM focuses on the front office, handling customer interactions, sales, and marketing.
What is the difference between ERP and CRM jobs?
While ERP looks inward to enhance overall operations, CRM is outward-facing, fostering strong client relationships and improving customer experiences. ERP is a back-office powerhouse, streamlining internal processes across departments like finance and supply chain. On the other hand, CRM is customer-centric, concentrating on sales, marketing, and customer service.
Is SAP a CRM or ERP system?
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a company that provides a range of enterprise software solutions, including both ERP and CRM systems. SAP offers products that fall into both categories. SAP CRM focuses on managing customer interactions and relationships, while SAP ERP streamlines business operations across various departments such as finance, procurement, and sales.
Related Posts: