Some claim that Google Tag Manager will make it much simpler for you to track visitors, while others guarantee that you won’t need developers any longer and can install tracking codes/pixels on your own. What’s the catch here?
Today, we will review and explain more about Google Tag Manager for Magento in this article. Let’s learn how you can add and configure the Google Tag Manager to your Magento 2 store.
Contents
What Is Google Tag Manager?

Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tag management system that includes the same functionality as global site tags. Simply put, GTM makes it easy to keep track of all the tags (or snippets of code) associated with your marketing campaign events.
As a result, you have direct access to measure your audience, personalize, retarget, or conduct search engine marketing campaigns.
Tag Manager includes tag organization and version control, third-party and community-developed tag templates, enterprise collaboration, and security features.
Google Tag Manager is divided into three sections:
- Tags: Javascript snippets or tracking pixels
- Triggers: The specific condition to add the tag (click, scroll, spend x seconds on-page, and more).
- Variables: Additional information for the tag and trigger to function properly.
How Does Google Tag Manager Work?
After having a GTM account, you need to generate GTM codes (or tags).
Then, you add the code generated to the <head> tag and the <body> of your website.
After that, a simple login to Google Tag Manager prevails the great range of possibilities of triggers. You can freely customize the trigger to one or a combination of user actions.
Then, each time the trigger sparks, the data will get “tagged” to the code and sent back to Google Analytics or a customizable third party with Google’s support.
What Can You Track with Google Tag Manager?
Based on your need, there is a myriad of data points you can track down with GTM. However, here are the 6 most common usages of GTM for an e-commerce website.
- Events (link clicks, PDF downloads, add to cart click, remove from cart click)
- Scroll tracking
- Incompleted form entry
- Cart abandonment
- Video view
- All exit link clicks
How Is Google Tag Manager Different From Google Analytics?
While the way they work seems similar at first, these two are not the same. While they are both necessary tools for your online store, GTM and Google Analytics (GA) are completely separated. You can use GTM to send collected events to a third-party outside of Google. GA is mainly for tracking data on a website.
However, since these two are both Google products, they are perfectly compatible. GTM is to deliver data and GA is to store and analyze data. At the same time, you do not need GTM to use Google Analytics.
Why Should You Use Magento 2 GTM On Your Store?
Simplify Tracking Process
The before-GTM-era was a dark time. Each time you launch a sales campaign, you would need to touch the source code to add the tracking agents.
And we all know meddling with the backbone of your Magento store at that frequency is a big no-no. Plus, each tracking code piece belongs to a different file that scatters everywhere.
Hence, Google Tag Manager is a huge game-changer. With the help of this handy tool, you can generate and tag various Magento 2 GTM in one place – no source code modification is required.
Deploy Testing Tools
Adding to the previous point, GTM also comes with a Preview & Debug mode. They let you double-check the tag before it goes live on your store.
This extra step eases the learning curve with GTM and allows store owners to set and run the tag easier, faster, and more secure.
Enhance Security with Magento 2 GTM
All tracking scripts added with Custom HTML tags in GTM accounts are automatically scanned by Google. Then, if they match a known malware (blacklisted) domain, IP address, or URL, Google will shut it down.
Furthermore, you are in charge of who has access to your GTM accounts and have the power to revoke that access at any time.
By including a few commands to your website’s data layer, you can also set up Allowlists or Blocklists. Since the website server is in charge of this, you will still have the final say regarding whether or not Custom Tracking Scripts are permitted to function on your site even if GTM is compromised.
Improve Site Performance
Here’s the thing, Magento 2 GTM only brings you the raw data based on your event settings. But what you can do with these data?
It’s pretty straightforward. If you track the conversion, more than the seer number, you’re able to know:
- The time it takes to complete an order
- How customers interact with your conversion path
- The after-purchase behaviors of the customers.
- And more.
With this knowledge, you’re more than capable of improving your website to lock the visitors on your site and turn them into customers.
Integrate With Google Analytics
These two will begin automatically listening to specific interactions on a web page as soon as you enable specific triggers in Google Tag Manager. There is still some setup necessary, but it is not too difficult. These interactions can be used to activate tracking codes, such as the Google Analytics Event Tag.
There’s still more, though! The number of auto-event tracking features is continuously growing due to the GTM user and enthusiast community. Additionally, you can include unique features that keep track of information like scroll depth, fresh comments, and more.
Why is this crucial? It enables you to learn more about the actions visitors take on your website, so to speak. Do they seem interested in the information? Do they complete your forms? Then, using these events, you can create goals in Google Analytics that are tailored to your company’s requirements.
How To Add Google Tag Manager To Magento 2 Website
Here are the 3 simple steps to implement GTM onto your Magento 2 Website.
- Step 1: Set up your Google Analytics account
- Step 2: Enable the Google Tag Manager account
- Step 3: Complete the setting in your Magento 2 store’s backend
Step 1: Set up your Google Analytics account
- Log into your Google Analytics account.
- Turn on the Internal Site Search Tracking, by following this instruction:
- Go to Select View > View Settings.
- Switch Site Search Tracking to On.
- Enter the Query parameter as
q. - When complete, click Save.
- In case you want to allow display features:
- Go to Property Settings.
- Within the Advertising Features branch, switch Enable Demographics and Interest Reports to On.
- Then Save.
- This one is important, to turn on Ecommerce Tracking, do the following:
- Go to Select View > Ecommerce Settings.
- Switch Enable Ecommerce to On.
- Switch Enable Enhanced Ecommerce Reporting to On.
- Save the process.
- To make sure that all the settings are still On, reload the page.
Step 2: Enable the Google Tag Manager account
- Save the file GTM_M2_Config_json.txt and do the following:
- Open the file in an editor app (you can use the Note on your window), and save it as
GTM_M2_Config.json. - Zip the file to produce an archive called
GTM_M2_Config.zip. The zipped file can directly go to Google Tag Manager. You don’t need to save a copy of this on your server.
- Open the file in an editor app (you can use the Note on your window), and save it as
- Go to Admin > Container > Import Container.
- Left-click to Choose container file and pick the json file.
- Within the Choose workspace, choose New.
- Fill in the title and description, then Save.
- Pick one of these 2 options to import the file:
- Overwrite option for a new container.
- Merge option for using a previous container.
- Choose Preview to double-check all 3 parts of your GTM: the tags, triggers, and variables.
- If you want to change the Google Analytics ID that is referenced in variables, do the following:
- Go to Variables > User-Defined Variables.
- Pick Google Analytics. Then, update the placeholder (UA-xxxxxx-x) with your GA ID.
- Continue the process with Google’s detailed instructions.
- Confirm once complete.
- Publish the new container accordingly.
Step 3: Complete the Magento 2 GTM setting in your store’s backend
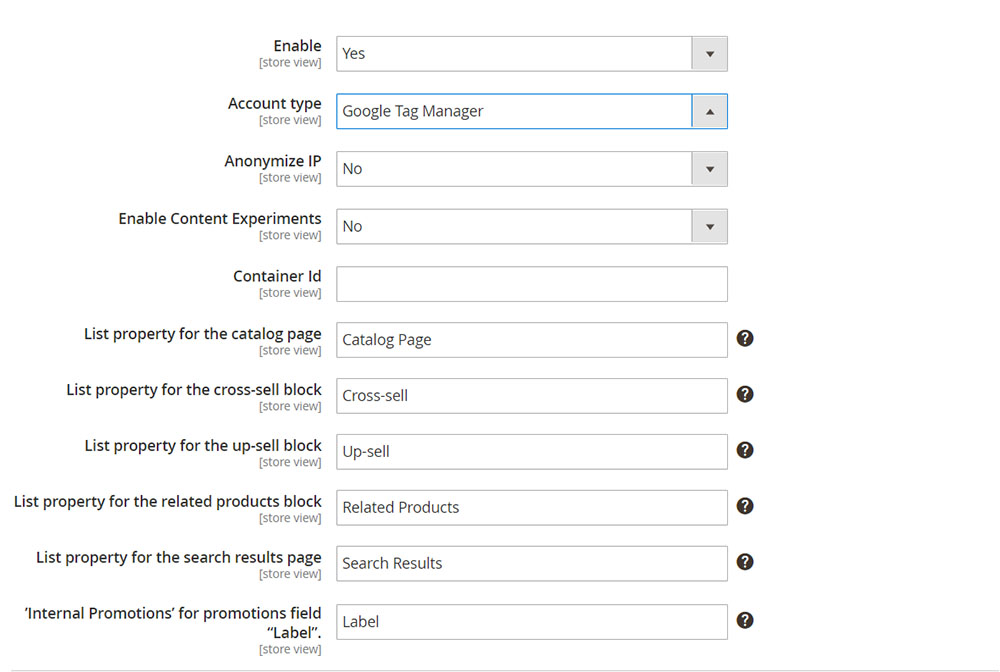
- Log into your Magento 2 backend.
- Navigate as following: Stores > Settings > Configuration.
- Expand Sales and click Google API.
- Expand the Google Analytics section and configure accordingly:
- Turn Enable to
Yes. - Choose the Account type as
Google Tag Manager. - In the Container ID field, fill in your GTM ID (
GTM-xxxxxx). - Set Enable Content Experiments
Yesif you set this up in your Google Analytics account. - The remaining fields can use the default value to proceed.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article has influenced your decision to start using GTM or your ability to persuade someone else to do so. Starting to use Google Tag Manager is definitely a no-brainer. Controlling tracking codes in one location is a comparatively simple solution.
For more useful Magento tutorials, make sure to subscribe to our blog. For any Magento-related questions, comment below or drop us a message at [email protected].
Tigren proudly brings you everything you need to improve your e-commerce store regardless of the framework you use. We believe in finding and deploying the best solution to uplift your business in performance, capacity, and scalability. Contact us with your request, our team is always happy to help!